For US Healthcare Professionals Only
Prescribing Information& Medication Guide Patient Site
Patients who took Vafseo achieved and sustained target Hb levels1
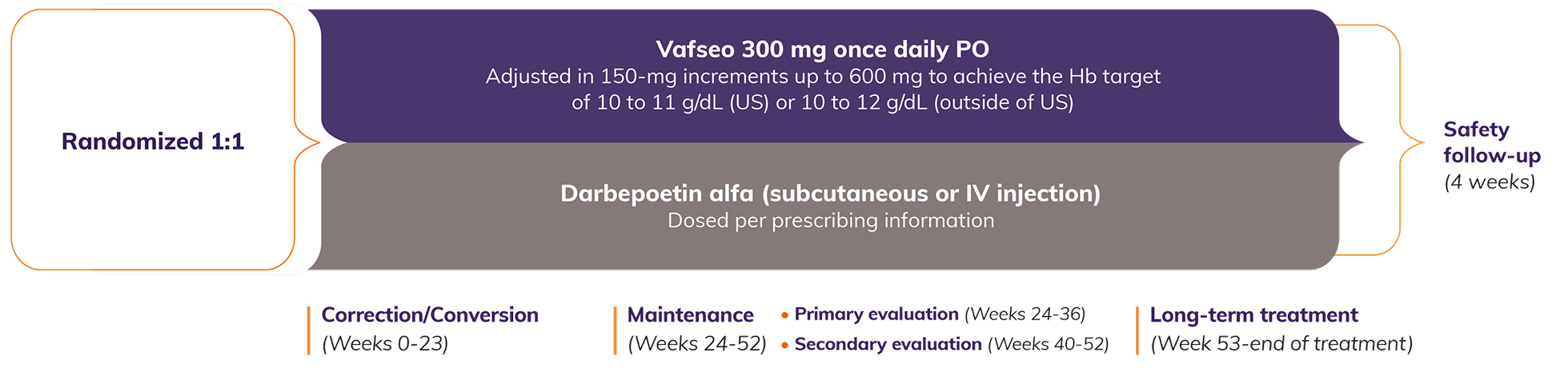
The efficacy and safety of Vafseo given once daily for the treatment of anemia in adults with CKD on dialysis were demonstrated in 2 global, multi-center, randomized, active-controlled, non-inferiority, open-label trials (N=3923). Trial endpoints included the difference in mean Hb change from baseline to primary evaluation period (Weeks 24 to 36) and secondary evaluation period (Weeks 40 to 52), and time to first occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE), using pre-specified, non-inferiority margins between Vafseo and darbepoetin alfa for both endpoints. While residual kidney function wasn’t measured, results were consistent across both trials and various dialysis durations in the Prevalent Dialysis Trial.1,2
Efficacy and safety of Vafseo were demonstrated in 2 pivotal Phase 3 trials1,2
Limitations: Residual kidney function was not measured, but results were uniform across both trials and various dialysis durations in the Prevalent Dialysis Trial.2
Key clinical trial endpoints1:
Efficacy:
Difference in mean change of Hb levels from baseline to primary (Weeks 24 to 36) and secondary (Weeks 40 to 52) evaluation periods, using the prespecified, noninferiority margin of -0.75 g/dL
Cardiovascular outcomes:
After 52 weeks, patients continued study medication. Time to first occurrence of MACE* was assessed in a pooled analysis of both trials, using the prespecified, noninferiority margin of 1.25
Key inclusion criteria1,2
| Incident Dialysis Trial
(INNO2VATE-1) | Prevalent Dialysis Trial (INNO2VATE-2) |
|---|---|
| Vafseo: n=181 Darbepoetin alfa: n=188 | Vafseo: n=1777 Darbepoetin alfa: n=1777 |
| Dialysis status | |
| Incident dialysis patient | Chronic maintenance dialysis patient |
| ≤16 weeks on dialysis | ≥12 weeks on dialysis |
| ESA status | |
| ESA-naïve, limited prior ESA use, or maintained on ESAs | Maintained on ESAs |
| Hb values | |
| 8 to 11 g/dL (US and outside the US) | 8 to 11 g/dL in the US; 9 to 12 g/dL outside the US |
| Iron status | |
| Serum ferritin ≥100 ng/mL and transferrin saturation ≥20% | Serum ferritin ≥100 ng/mL and transferrin saturation ≥20% |
CKD=chronic kidney disease; ESA=erythropoiesis-stimulating agent.
Key exclusion criteria2
Patients with anemia due to non-CKD causes, uncontrolled hypertension, or a recent cardiovascular event were excluded from the trials.
Select baseline characteristics of patients in the clinical trials1,2
| Incident Dialysis Trial (INNO2VATE-1) | Prevalent Dialysis Trial (INNO2VATE-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Vafseo (N=181) | Darbepoetin alfa (N=188) | Vafseo (N=1777) | Darbepoetin alfa (N=1777) |
| Age, years | 56.5 ± 14.8 | 55.6 ± 14.6 | 57.9 ± 13.9 | 58.4 ± 13.8 |
| Male sex, number (%) | 107 (59.1) | 113 (60.1) | 990 (55.7) | 1004 (56.5) |
| Time since dialysis initiated, years | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.15 ± 0.28 | 4.00 ± 4.02 | 3.94 ± 4.01 |
| Racial or ethnic group, number (%)† | ||||
| Caucasian | 129 (71.3) | 143 (76.1) | 1135 (63.9) | 1096 (61.7) |
| Black (including African Americans) | 38 (21.0) | 35 (18.6) | 432 (24.3) | 444 (25.0) |
| Asian | 12 (6.6) | 8 (4.3) | 76 (4.3) | 99 (5.6) |
| Hispanic | 71 (39.2) | 66 (35.1) | 682 (38.4) | 674 (37.9) |
| Type of dialysis, number (%)‡ | ||||
| In-center hemodialysis | 158 (87.3) | 169 (90.9) | 1652 (93.0) | 1633 (91.9) |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 22 (12.2) | 16 (8.6) | 137 (7.7) | 143 (8.0) |
| Unknown or combination | 3 (1.7) | 1 (0.5) | 17 (1.0) | 18 (1.0) |
| Disease history, number (%) | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 105 (58.0) | 96 (51.1) | 971 (54.6) | 998 (56.2) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 69 (38.1) | 73 (38.8) | 868 (48.8) | 932 (52.4) |
| Hb concentration, g/dL | 9.4 ± 1.1 | 9.2 ± 1.1 | 10.3 ± 0.9 | 10.2 ± 0.8 |
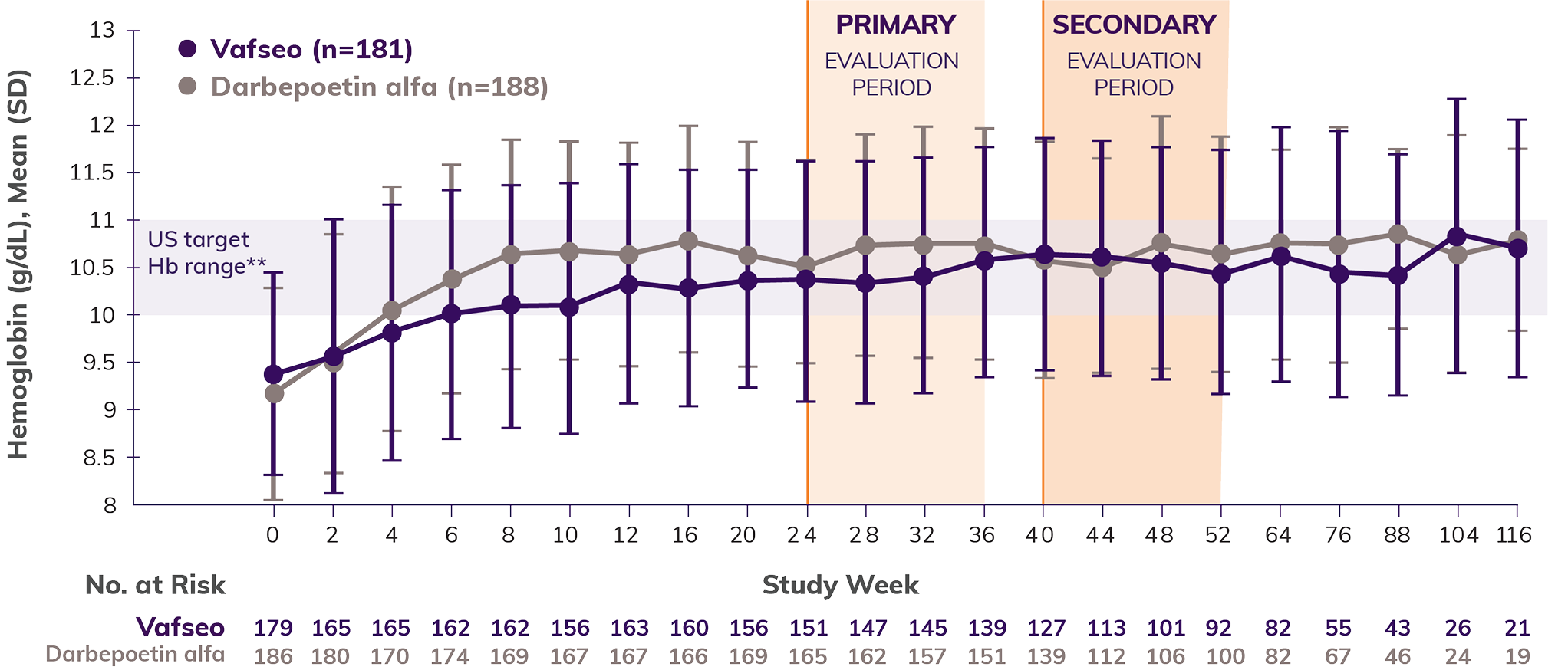
Efficacy shown through 52 weeks: Incident Dialysis Trial (INNOV2VATE-1)
Patients who took Vafseo achieved and sustained target Hb levels1
Noninferiority of Vafseo§ compared to an ESA|| was established at Weeks 24-36 and Weeks 40-52 because the lower bound of the 95% CI for the treatment difference in mean change in Hb from baseline was less than the prespecified, noninferiority margin of -0.75 g/dL.1
Mean Hb levels over time1-3,#


TAP TO EXPAND
ROTATE DEVICE FOR LARGEST VIEW

TAP TO EXPAND
ROTATE DEVICE FOR LARGEST VIEW
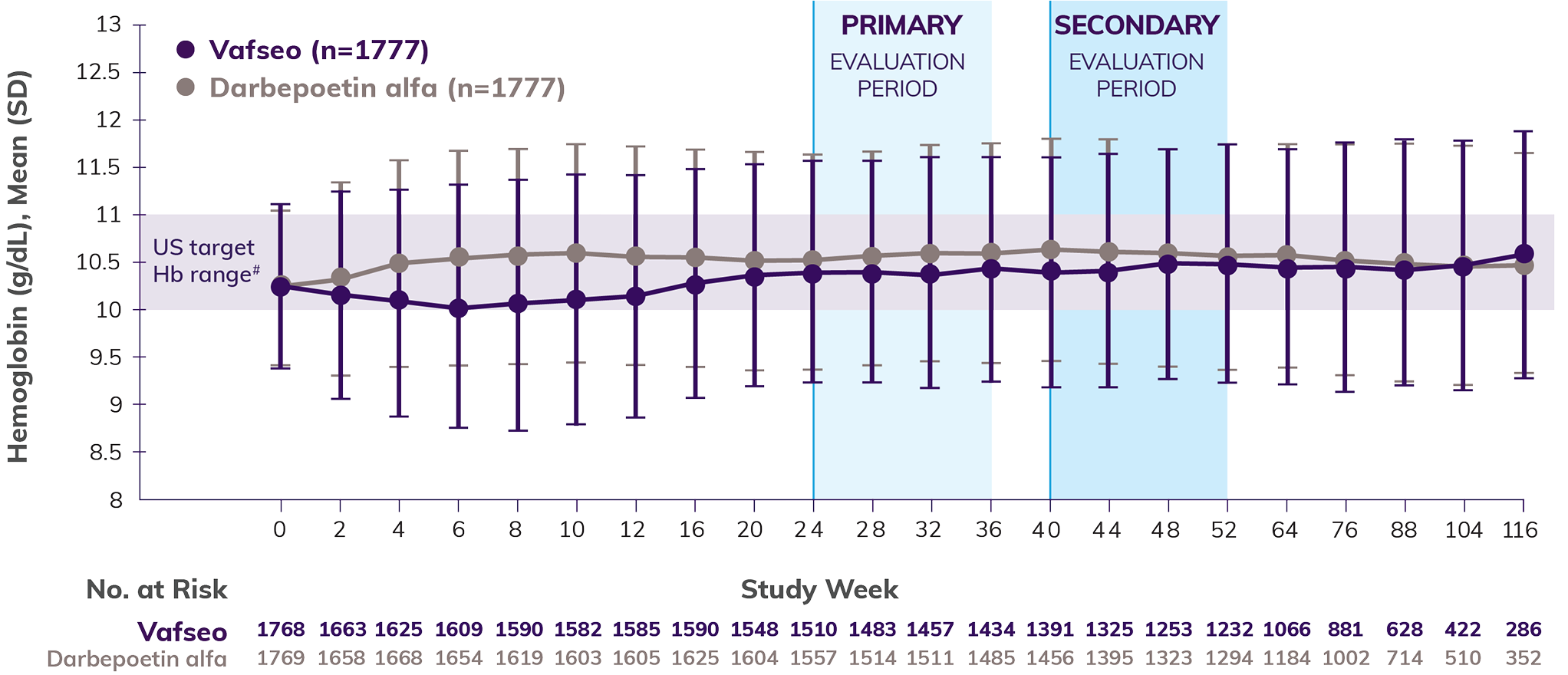
Efficacy shown through 52 weeks: Prevalent Dialysis Trial (INNOV2VATE-2)
Patients who took Vafseo achieved and sustained target Hb levels1
Noninferiority of Vafseo compared to an ESA§ was established at Weeks 24-36 and Weeks 40-52 because the lower bound of the 95% CI for the treatment difference in mean change in Hb from baseline was less than the prespecified, noninferiority margin of -0.75 g/dL.1
Mean Hb levels over time1-3,||


TAP TO EXPAND
ROTATE DEVICE FOR LARGEST VIEW

TAP TO EXPAND
ROTATE DEVICE FOR LARGEST VIEW
The data show an initial transient decrease in mean Hb in the Vafseo arm during the correction/conversion phase. All patients were started on a standardized dose of 300 mg once daily, regardless of prior ESA dosage. In the trial, investigators could only titrate up every 4 weeks and in increments of 150 mg.1,3,4
-
Approximately 35% of patients experienced a decrease in Hb levels of 0.5 g/dL or more at week 4 in the Prevalent Dialysis Trial**—especially in those previously maintained on high doses of ESAs (≥300 U/kg/week of IV epoetin equivalent unit)3,4,††
-
The mean Hb for the study population began to rise by week 82
-
By week 12, more than half of patients were taking 450 mg or 600 mg4,††,‡‡
It’s important to anticipate a potential dip, which may serve as an opportunity to review dosing and titration, consistent with the Vafseo Prescribing Information.1

WARNING: INCREASED RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS
THROMBOEMBOLISM, and THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS.
VAFSEO increases the risk of thrombotic vascular events, including major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Targeting a hemoglobin level greater than 11 g/dL is expected to further increase the risk of death and arterial and venous thrombotic events, as occurs with erythropoietin stimulating agents (ESAs), which also increase erythropoietin levels.
No trial has identified a hemoglobin target level, dose of VAFSEO, or dosing strategy that does not increase these risks.
Use the lowest dose of VAFSEO sufficient to reduce the need for red blood cell transfusions.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Known hypersensitivity to VAFSEO or any of its components
- Uncontrolled hypertension
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Increased Risk of Death, Myocardial Infarction (MI), Stroke, Venous Thromboembolism, and Thrombosis of Vascular AccessA rise in hemoglobin (Hb) levels greater than 1 g/dL over 2 weeks can increase these risks. Avoid in patients with a history of MI, cerebrovascular event, or acute coronary syndrome within the 3 months prior to starting VAFSEO. Targeting a Hb level of greater than 11 g/dL is expected to further increase the risk of death and arterial and venous thrombotic events. Use the lowest effective dose to reduce the need for red blood cell (RBC) transfusions. Adhere to dosing and Hb monitoring recommendations to avoid excessive erythropoiesis.
- HepatotoxicityHepatocellular injury attributed to VAFSEO was reported in less than 1% of patients, including one severe case with jaundice. Elevated serum ALT, AST, and bilirubin levels were observed in 1.8%, 1.8%, and 0.3% of CKD patients treated with VAFSEO, respectively. Measure ALT, AST, and bilirubin before treatment and monthly for the first 6 months, then as clinically indicated. Discontinue VAFSEO if ALT or AST is persistently elevated or accompanied by elevated bilirubin. Not recommended in patients with cirrhosis or active, acute liver disease.
- HypertensionWorsening of hypertension was reported in 14% of VAFSEO and 17% of darbepoetin alfa patients. Serious worsening of hypertension was reported in 2.7% of VAFSEO and 3% of darbepoetin alfa patients. Cases of hypertensive crisis, including hypertensive encephalopathy and seizures, have also been reported in patients receiving VAFSEO. Monitor blood pressure. Adjust anti-hypertensive therapy as needed.
- SeizuresSeizures occurred in 1.6% of VAFSEO and 1.6% of darbepoetin alfa patients. Monitor for new-onset seizures, premonitory symptoms, or change in seizure frequency.
- Gastrointestinal (GI) ErosionGastric or esophageal erosions occurred in 6.4% of VAFSEO and 5.3% of darbepoetin alfa patients. Serious GI erosions, including GI bleeding and the need for RBC transfusions, were reported in 3.4% of VAFSEO and 3.3% of darbepoetin alfa patients. Consider this risk in patients at increased risk of GI erosion. Advise patients about signs of erosions and GI bleeding and urge them to seek prompt medical care if present.
- Serious Adverse Reactions in Patients with Anemia Due to CKD and Not on DialysisThe safety of VAFSEO has not been established for the treatment of anemia due to CKD in adults not on dialysis and its use is not recommended in this setting. In large clinical trials in adults with anemia of CKD who were not on dialysis, an increased risk of mortality, stroke, MI, serious acute kidney injury, serious hepatic injury, and serious GI erosions was observed in patients treated with VAFSEO compared to darbepoetin alfa.
- MalignancyVAFSEO has not been studied and is not recommended in patients with active malignancies. Malignancies were observed in 2.2% of VAFSEO and 3.0% of darbepoetin alfa patients. No evidence of increased carcinogenicity was observed in animal studies.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most common adverse reactions (occurring at ≥ 10%) were hypertension and diarrhea.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Iron supplements and iron-containing phosphate binders: Administer VAFSEO at least 1 hour before products containing iron.
- Non-iron-containing phosphate binders: Administer VAFSEO at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after non-iron-containing phosphate binders.
- BCRP substrates: Monitor for signs of substrate adverse reactions and consider dose reduction.
- Statins: Monitor for statin-related adverse reactions. Limit the daily dose of simvastatin to 20 mg and rosuvastatin to 5 mg.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm.
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended until two days after the final dose.
- Hepatic Impairment: Not recommended in patients with cirrhosis or active, acute liver disease
VAFSEO is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney disease (CKD) in adults who have been receiving dialysis for at least three months.
Limitations of Use
- VAFSEO has not been shown to improve quality of life, fatigue, or patient well-being.
- VAFSEO is not indicated for use:
- As a substitute for red blood cell transfusions in patients who require immediate correction of anemia.
- In patients with anemia due to CKD not on dialysis.
Please note that this information is not comprehensive. Please click here for the Full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING and Medication Guide.